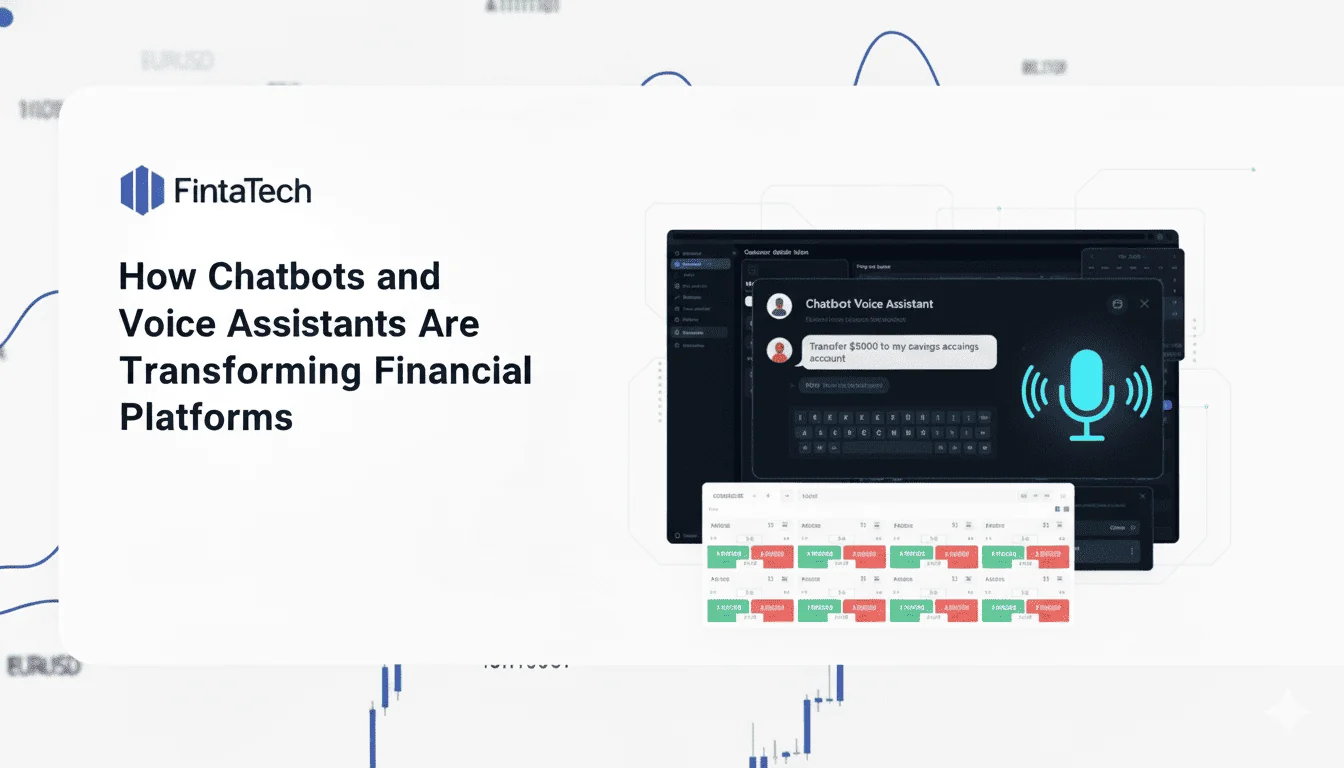
The financial industry has always been a technology frontrunner — from ATMs to online banking, every decade brings innovations that redefine how people manage money. But few innovations have had as profound and humanizing an impact as chatbots and voice assistants.
In an era where customers expect 24/7 access, instant responses, and personalized experiences, conversational AI has become the bridge between digital convenience and human-like interaction. Banks, trading platforms, and fintech startups are integrating these tools not only to handle customer requests but also to provide proactive financial insights, risk monitoring, and personalized investment guidance.
According to Juniper Research, financial institutions are projected to save over $7 billion annually by 2028 through AI-powered conversational systems. But cost-cutting is just one aspect — the real transformation lies in how chatbots and voice assistants are reshaping the user experience and business operations across the financial ecosystem.
From Support Tool to Strategic Asset
At first, chatbots were simple FAQ engines — answering basic questions and routing users to the right department. Today, powered by large language models (LLMs) and advanced NLP frameworks, they’ve evolved into intelligent digital agents capable of complex, context-aware communication.
- Financial institutions now deploy chatbots that can:
- Execute real-time transactions securely.
- Analyze customer behavior to recommend personalized financial products.
- Detect anomalies or potential fraud through conversational cues.
- Support compliance processes such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering).
Similarly, voice assistants have moved beyond simple command execution. Integrated with banking apps, smart devices, and embedded fintech platforms, they allow users to speak naturally:
“What’s my portfolio performance this month?”
“Transfer $200 from savings to checking.”
“How much did I spend on subscriptions last quarter?”
The result is frictionless finance — seamless access, hands-free functionality, and intuitive engagement that mirrors how humans communicate.
Core Benefits for Financial Platforms
Before diving into specific use cases, it’s important to understand why conversational AI has become a cornerstone of modern financial platforms. Chatbots and voice assistants don’t just enhance convenience, they fundamentally reshape how institutions deliver services, manage data, and interact with customers at scale. Below are the core benefits driving widespread adoption across the financial sector.
- Always-On Customer Engagement
In a global market, users operate across time zones. Chatbots offer round-the-clock support, enabling consistent service without requiring full-time human agents.
This is especially powerful for trading platforms or fintech apps like Fintatech’s Trading Platform Designer, where response time directly affects user satisfaction and retention. - Operational Efficiency & Cost Reduction
Conversational AI automates 60–80% of routine interactions. This frees human agents to focus on high-value activities such as client onboarding, financial advising, or dispute resolution.
According to IBM, businesses using chatbots can reduce customer service costs by up to 30%, while improving accuracy and speed. - Hyper-Personalization at Scale
Financial users want more than automation — they want relevance. Chatbots analyze transaction data, spending habits, and portfolio patterns to deliver personalized recommendations such as savings tips, loan optimization, or investment opportunities.
For instance, an AI assistant might suggest:
“You could save $240 annually by consolidating your credit cards,”
or
“Your tech ETF underperformed last quarter. Would you like a market summary?” - Enhanced Security and Trust
Voice biometrics, sentiment analysis, and two-factor conversational authentication make AI assistants both convenient and secure. Modern systems can detect emotional stress in a user’s tone, identifying potential fraud or account takeover attempts. - Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Chatbots can log every interaction automatically — a key advantage for audit trails, GDPR compliance, and dispute resolution. They also assist with regulatory workflows like client verification and data privacy consent. - Streamlined Internal Processes
AI agents aren’t just customer-facing. They help financial teams automate document verification, risk scoring, and CRM updates. For example, internal assistants can summarize complex financial reports, pull KPIs from data warehouses, or flag anomalies in client portfolios.
Real-World Use Cases
| Use Case | Example / Functionality | Business Impact |
|---|
| Retail Banking Chatbots | Handle balance inquiries, transaction summaries, and card blocking. | Reduces call center volume by up to 50%. |
| Voice-Enabled Banking | Hands-free commands via smart speakers or apps (e.g., Alexa, Siri). | Improves accessibility and user convenience. |
| Investment Advisory Assistants | Provide market insights, suggest portfolio rebalancing, track trends. | Enhances engagement and retention for investors. |
| Customer Onboarding Automation | Guide users through KYC verification, document upload, and account setup. | Shortens onboarding from days to minutes. |
| Internal Compliance Bots | Audit data consistency, flag irregularities, or prepare compliance reports. | Increases accuracy, reduces manual workload. |
| Insurance and Lending | Estimate loan eligibility, provide quote comparisons, remind about payments. | Boosts conversion and lifetime value. |
For example, Bank of America’s Erica, one of the world’s most successful financial chatbots, handles over 1 billion interactions annually, providing balance checks, transaction insights, and proactive alerts.
Similarly, Capital One’s Eno uses natural conversation to help users track spending, manage bills, and even detect suspicious transactions.
Challenges in Adopting Conversational AI
While adoption is accelerating, implementation comes with challenges unique to the financial sector.
While adoption is accelerating, implementation comes with challenges unique to the financial sector.
- Data Security & Privacy Concerns
AI assistants process sensitive information. Ensuring end-to-end encryption, secure data storage, and compliance with global privacy frameworks (GDPR, CCPA, PSD2) is critical. - Integrating Legacy Infrastructure
Many banks and trading systems rely on legacy architectures that were not designed for API-driven integration. Fintech platforms must implement middleware layers or microservices to bridge old and new systems effectively. - Maintaining Human Empathy
AI may simulate conversation but lacks genuine emotional understanding. Financial decisions are often emotional — loans, investments, losses — so balancing automation with human empathy remains key. - Regulatory Complexity
Each jurisdiction has unique compliance rules around digital interactions, record-keeping, and data retention. Voice assistants in particular must adhere to local data processing laws. - Over-Automation Risks
Not every task should be automated. If chatbots replace too much human interaction, it can lead to user frustration, especially for complex issues that require contextual judgment or negotiation.
Implementation Framework: A Strategic Roadmap
To deploy conversational AI successfully, financial platforms should follow a structured implementation model.
Phase 1: Discovery & Assessment
– Define clear goals — whether to improve customer support, automate onboarding, or increase retention.
– Identify user pain points and operational bottlenecks.
– Audit your current data infrastructure and API readiness.
Phase 2: Design & MVP Development
– Build a prototype with limited functionality — e.g., FAQ automation or account balance retrieval.
– Choose an NLP framework suited for financial language (Dialogflow, Rasa, or OpenAI-based models).
– Ensure multilingual support if your platform serves multiple regions.
Phase 3: Integration & Security
– Connect with internal systems (CRM, payments, analytics, KYC).
– Implement multi-factor authentication and encryption protocols.
– Establish secure access policies and role-based permissions.
Phase 4: Training & Optimization
– Train your chatbot using anonymized, real conversation data to improve contextual understanding.
– Continuously fine-tune based on customer feedback, intent recognition, and analytics.
Phase 5: Monitoring & Governance
– Track performance metrics such as resolution rate, average handling time, escalation ratio, and satisfaction (CSAT).
– Maintain transparency logs for audit and compliance purposes.
– Update models regularly to adapt to new products and regulations.
Phase 6: Expansion & Innovation
– Add new capabilities like voice interactions, predictive analytics, and emotional recognition.
– Integrate with third-party fintech APIs for trading, investing, or insurance.
– Consider using agentic AI — intelligent systems that can execute multi-step tasks autonomously (e.g., reviewing transactions, generating portfolio reports).
The Future of Conversational Finance
The evolution of chatbots and voice assistants is just beginning. Here’s what lies ahead:
- Voice-First Finance
As smart devices become ubiquitous, voice will overtake text as the dominant interaction mode. Imagine a trading platform where users say, “Show me top-performing AI stocks this week,” and the system executes instant queries with contextual insights. - Predictive & Proactive Assistance
Next-gen AI won’t wait for users to ask questions — it will anticipate needs. For instance, alerting customers before overdrafts occur or suggesting refinancing options based on market rates. - Emotional & Contextual Awareness
With sentiment analysis, chatbots will soon adapt tone and responses to match user emotions — offering empathy in stressful moments or excitement during milestones. - Embedded Conversational Finance
Financial services will integrate directly into other ecosystems: e-commerce, travel, real estate, through APIs and voice interactions. Users will make payments or investments without leaving their current app or platform. - Autonomous Financial Agents
Agentic AI will move beyond reactive support. These systems will manage tasks independently: from rebalancing portfolios to identifying investment anomalies — acting as intelligent financial copilots.
Conclusion
Chatbots and voice assistants are redefining financial services from the ground up. They streamline operations, empower customers with real-time data, and open new possibilities for personalization and accessibility.
However, success requires more than deploying a chatbot — it demands a strategic, secure, and human-centered approach. The most forward-thinking fintechs will view conversational AI not as a cost-saving tool, but as a core enabler of value creation and customer loyalty. The future of finance is conversational, and the conversation has only just begun.

Twitter
Linkedin
Facebook