Proprietary trading, often referred to as “prop trading,” involves financial institutions engaging directly in the markets using their own capital, rather than that of their clients. This method of trading is distinct from traditional brokerage services and allows institutions to capitalize on market opportunities through direct participation. The purpose of this article is to delve into the nuances of proprietary trading, exploring how it operates, its inherent benefits and challenges, and the steps involved in establishing a prop trading firm.
What Is Proprietary Trading?
Proprietary trading, often called “prop trading,” is when a financial firm or bank trades stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, their derivatives, or other financial instruments, with its own money instead of its clients’ money, so as to make a profit for itself. Unlike traditional stockbrokers or investment advisors who trade on behalf of their clients and earn commissions for the services provided, proprietary trading desks invest the firm’s own capital.
The primary goal of prop trading is to generate direct profits from the markets. This type of trading allows firms to leverage specialized strategies ranging from arbitrage and swing trading to algorithmic and high-frequency trading techniques. Because the firm uses its own capital, it assumes the full risk of its trading activities. The rewards can be significant, but the risks are equally high, especially since proprietary trading can involve speculative strategies that may result in substantial losses.
How Does Proprietary Trading Work?
Proprietary trading works by financial institutions using their own capital to trade financial instruments with the goal of realizing a profit from market activities. Here’s how it typically operates:
- Capital Allocation: The firm allocates its own capital specifically for trading purposes, separating it from client funds and other operational funds. This capital is used to take positions in the market.
- Trading Strategies: Traders at the firm employ various strategies depending on the firm’s expertise and risk tolerance. Common strategies include:
- Market Making: Traders buy and sell financial instruments to provide liquidity to the markets, earning profits on the bid-ask spread.
- Arbitrage: This involves buying and selling the same or similar securities simultaneously in different markets or in different forms to capitalize on price differences without significant risk.
- Swing Trading: This strategy involves holding positions for several days to capitalize on expected upward or downward market shifts.
- Quantitative and Algorithmic Trading: Using mathematical models to identify trading opportunities, often executed via automated trading systems.
- Directional Trading: This involves taking a long or short position on a financial instrument based on predictions of future price movements.
- Risk Management: Since proprietary trading involves substantial risks, firms implement rigorous risk management strategies. These include setting limits on the size of trades, continuously monitoring positions, and using hedging techniques to mitigate potential losses.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Prop trading often requires sophisticated technological infrastructure, including high-speed trading platforms, advanced data analytics tools, and robust security systems. This infrastructure supports the rapid execution of trades and real-time monitoring of market conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Firms engaging in proprietary trading must comply with various regulations, such as the Volcker Rule in the United States, which restricts certain kinds of speculative investments made by banks. Compliance involves regular reporting and ensuring that the trading activities do not conflict with the interests of their clients.
- Profit and Loss (P&L) Tracking: Daily tracking of profits and losses is crucial. The success of proprietary trading is measured by the ability to generate consistent profits over time.
Benefits of Proprietary Trading
Proprietary trading desks operate independently of client-facing parts of the firm, such as investment banking or advisory services, which allows them to focus solely on trading activities. The high-risk nature of this type of trading means that while the potential for profit is significant, the potential for loss is equally substantial.
Benefits of Proprietary Trading
Proprietary trading offers several benefits to financial institutions that engage in it, despite the inherent risks. Here are some of the key advantages:
Profit Potential: One of the primary benefits of proprietary trading is the potential for high profits. Since firms use their own capital to trade, they retain all the gains from successful trades, unlike client-based trading where the firm earns a commission regardless of the outcome.
Full Control and Autonomy: Proprietary trading gives firms full control over their trading decisions and strategies. This autonomy allows firms to execute trades based on their own analysis and forecasts without the need to align with client preferences or risk tolerance.
Market Liquidity: Prop traders often act as market makers in various securities, providing liquidity to the markets. This helps in maintaining efficient markets, as it reduces the bid-ask spread that traders encounter, facilitating smoother and quicker transactions for other market participants.
Diversification of Revenue: Proprietary trading can serve as an important source of diversification for a financial institution’s revenue streams. It can provide a balance to traditional revenue sources such as commissions and fees from client services, particularly during times when commission-based revenues are lower.
Leveraging Expertise: Financial institutions can leverage their in-house research, trading expertise, and technological infrastructure to maximize returns through proprietary trading. This includes using advanced quantitative models and high-frequency trading systems that might not be available to average investors.
Innovation in Trading Strategies: Since prop trading desks are not restricted by client mandates, they have the freedom to innovate and develop new trading strategies and technologies. This can include exploring emerging markets, new financial instruments, and cutting-edge trading technologies.
Risk Management Skills: Engaging in proprietary trading requires robust risk management practices. This can enhance the firm’s overall risk management capabilities, benefiting other areas of the business through improved practices and technologies.
Testing Ground for Trading Strategies: Proprietary trading allows firms to test and refine trading strategies in a real-world environment without external client implications. Successful strategies can later be adapted to client-focused services.

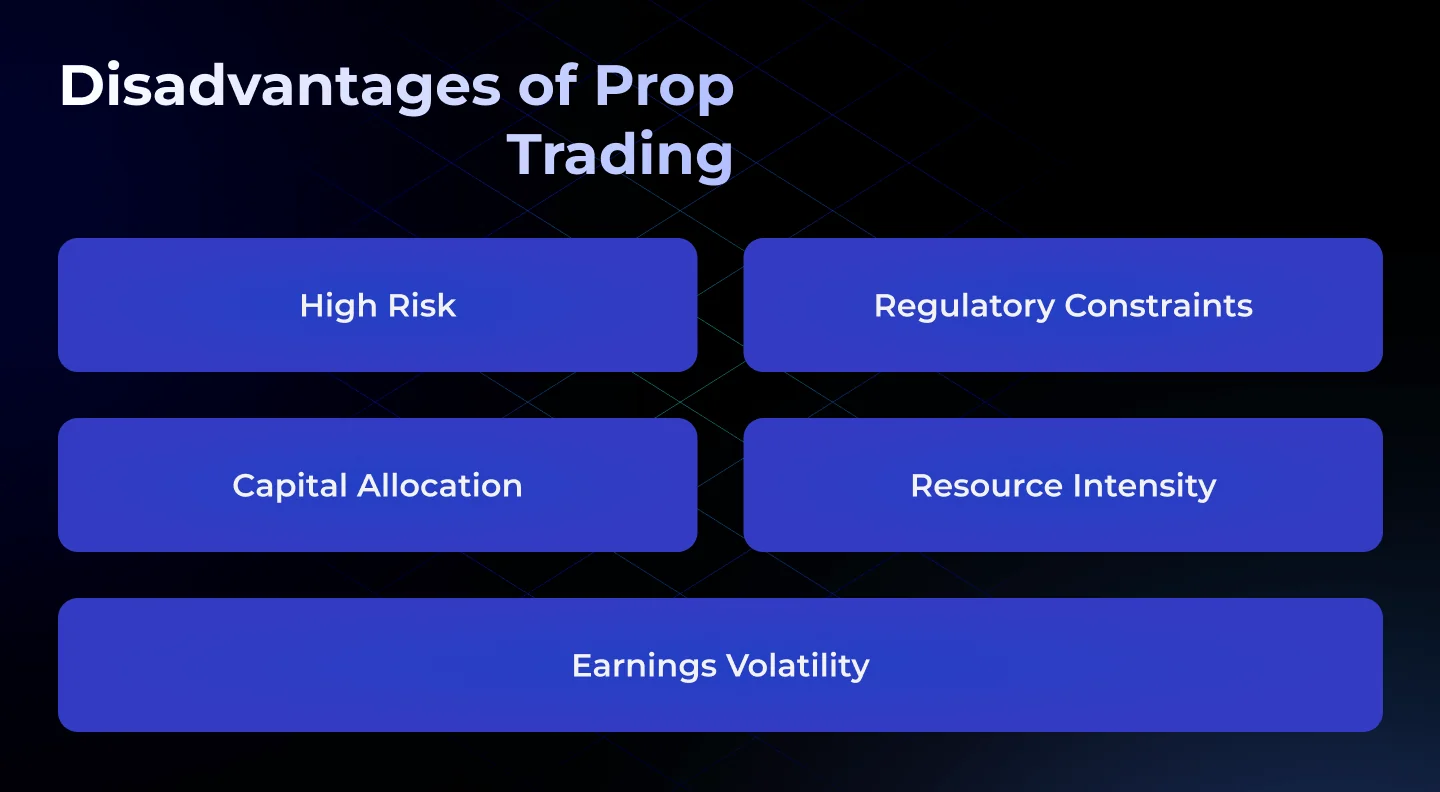
Disadvantages of Prop Trading
Proprietary trading, while potentially lucrative, also presents several significant disadvantages:
- High Risk: Direct financial impacts from losses can be substantial due to volatile trading strategies.
- Regulatory Constraints: Stricter regulations like the Volcker Rule limit the scope and profitability of prop trading.
- Conflict of Interest: Potential conflicts may arise between a firm’s trading activities and client interests.
- Capital Allocation: Funds used for prop trading could be deployed in other, potentially less risky, business areas.
- Market Impact: Large trades can influence market prices, affecting overall market stability.
- Reputational Risk: High-profile losses can damage a firm’s reputation and undermine client confidence.
- Resource Intensity: Requires significant investment in technology and skilled personnel.
- Earnings Volatility: Profits from prop trading can fluctuate widely, making financial planning more challenging.
Due to these disadvantages, many firms weigh the potential gains from proprietary trading against the risks and costs associated with it. Some choose to limit or scale down their prop trading activities, focusing instead on less risky, client-driven business models.
Starting a Proprietary Trading Firm: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Industry Knowledge and Initial Planning:
- Begin by gaining a deep understanding of the financial industry. Enhance your trading and investing skills.
- Develop high-level business ideas and then distill these into a detailed business plan outlining your objectives and strategies.
- Legal Registration:
- Register your company following local and international regulations to ensure legal compliance.
- Technological Setup:
- Choose and set up the trading technology for your operations and client services. This technology should help manage your trading exposure and client interactions.
- Hiring Key Personnel:
- Recruit a capable team to manage various departments including dealing, helpdesk, and marketing.
- Marketing and Client Acquisition:
- Develop and execute a marketing strategy, launch your website, and begin attracting clients.
- Risk Management:
- Establish a robust risk management strategy and identify key client targets for initial evaluations.
Selecting the Ideal Technology for Your Proprietary Trading Firm
Implementing the right technology is crucial for successfully launching and managing a proprietary trading firm. A comprehensive prop trading platform can offer an all-in-one solution, facilitating effective management of client interactions and trading exposure while ensuring a professional trading experience for both staff and clients.
Technology for Staff:
- Automated Risk Management: Implement risk management tools that operate in real time, allowing for automated adjustments based on maximum drawdowns and profit targets.
- Trading Simulation Environment: Before allocating real funds, use a trading simulation to assess and train your clients, ensuring they are prepared for live trading scenarios.
- Operational Dashboard: Equip your staff with a central dashboard to manage traders and overall trading operations efficiently.
- Automated Trading Contests: Engage and motivate traders by automatically setting up trading contests that encourage performance and skill development.
Technology for Clients:
- Professional Trading Platform: Provide a state-of-the-art trading platform that enhances the trading experience, making clients feel like professional traders.
- Activity Tracking Widgets: Offer widgets that allow traders to monitor their trading activity and performance in real time.
- Technical Analysis Tools: Equip your platform with comprehensive technical analysis tools to help traders make informed decisions.
- Advanced Charting: Include advanced charting capabilities with both turnkey and customizable indicators, catering to the needs of novice and experienced traders alike.
Choosing a platform that integrates these features will not only streamline your operational processes but also attract and retain skilled traders by providing them with the tools they need to succeed.
Benefits of White-label Prop Firms
White-label solutions for proprietary trading firms offer several significant benefits that can enhance the business model, streamline operations, and offer competitive advantages in the financial markets. Here are some key benefits of adopting a white-label approach for prop trading firms:
- Cost Efficiency: White-label platforms eliminate the need for extensive research and development costs associated with building a proprietary system from scratch. By using a pre-built platform that can be branded as their own, prop trading firms can save on development costs and allocate resources more effectively elsewhere.
- Quick Market Entry: White-label solutions allow firms to launch their operations much faster than if they were to develop their own technology. This quick setup is crucial in the fast-paced trading world, enabling firms to capitalize on market opportunities without delay.
- Proven Technology: By opting for a white-label solution, prop trading firms can leverage proven technologies that have been tested and refined over time. This reduces the risks associated with deploying untested systems and ensures a more reliable and robust trading environment.
- Customization and Branding: While the underlying technology is provided by another provider, white-label platforms can often be customized to meet the specific needs of the firm. This includes branding the platform with the firm’s logo, colors, and other corporate identity elements to maintain a consistent brand image.
- Access to Advanced Features: White-label platforms typically come equipped with advanced trading tools and features, such as real-time data, sophisticated charting, risk management systems, and automated trading options. These features would be costly and time-consuming to develop independently.
- Scalability: White-label solutions are designed to be scalable, accommodating growth without the need for significant additional investment. As the trading firm expands, the platform can easily handle increased trading volume and additional users.
- Support and Maintenance: Vendors of white-label platforms usually provide ongoing support and maintenance, ensuring that the platform operates smoothly and stays updated with the latest technological advancements and security protocols.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many white-label solutions come with built-in compliance features that adhere to relevant financial regulations. This is particularly beneficial for prop trading firms, as it reduces the burden of ensuring compliance through internal resources.
- Focus on Core Business: With the technical aspects handled by the white-label provider, prop trading firms can focus more on their core business activities such as strategy development, client acquisition, and trading operations.
- Professional Experience for Traders: Ultimately, a robust white-label platform provides a professional trading experience for traders, which can enhance the firm’s reputation and attractiveness to both new and experienced traders.
By leveraging white-label solutions, proprietary trading firms can achieve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and offer a competitive service, all while maintaining a strong focus on their trading strategies and client services.
Conclusion
Proprietary trading represents a dynamic and potentially lucrative aspect of the financial world, providing institutions with the autonomy to execute diverse strategies and realize significant profits. However, it also brings with it considerable risks and regulatory responsibilities. Firms that choose to engage in prop trading must adeptly manage these risks and adhere to stringent regulations to safeguard their operations and reputation. For those considering starting a prop trading firm, understanding the market intricacies, choosing the right technology, and developing effective risk management strategies are critical steps. By balancing these elements, proprietary trading firms can not only survive but thrive, driving innovation and efficiency in the financial markets.


Twitter
Linkedin
Facebook